Boeing's Starliner finally ready for first crewed mission

Launch day is finally here: Boeing's Starliner capsule blasts off Monday to the International Space Station on its first crewed mission -- several years after SpaceX first achieved the same milestone.
The flight, a final test before Starliner takes up regular service for NASA, is critical for the US aerospace giant, whose reputation has suffered of late due to safety issues with some of its passenger jets.
Starliner, which was first ordered a decade ago by the US space agency, has had a bumpy ride to the finish line, with surprise setbacks and multiple delays -- a saga Boeing is eager to complete.
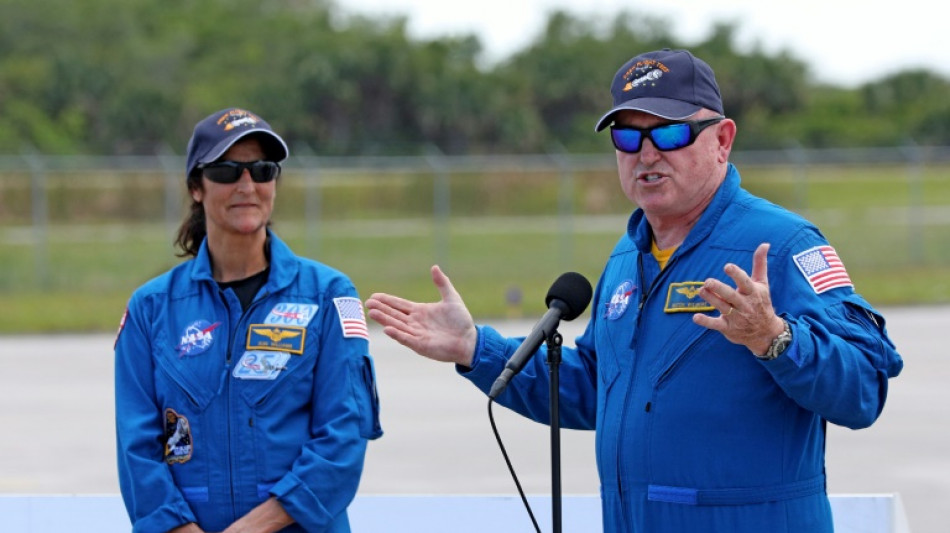
Astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are set to leave Cape Canaveral at 10:34 pm Monday (0234 GMT Tuesday) aboard the capsule.
Starliner will be propelled into orbit by an Atlas V rocket made by United Launch Alliance, a Boeing-Lockheed Martin joint venture.
Wilmore and Williams, Navy-trained space program veterans, have each been to the ISS twice, traveling once on a shuttle and then aboard a Russian Soyuz vessel.
"It's going to be like going back home," Williams said.
As for the Boeing spacecraft, Wilmore said: "Everything is new. Everything's unique."
"I don't think either one of us ever dreamed that we'd be associated with the first flight of a brand new spacecraft."
For NASA, the stakes are also high: Having a second option for human space flight in addition to SpaceX's Dragon vehicles is "really important," said Dana Weigel, manager of the agency's International Space Station program.
Weigel said the flexibility could help NASA manage emergency situations, such as problems with a particular space vehicle.
- Setback after setback -
Starliner is scheduled to arrive at the ISS at about 0500 GMT Wednesday, and remain there for a little over a week. Tests will be performed to check it is working properly, and then Williams and Wilmore will reboard the capsule to return home.
A successful mission would help dispel the bitter taste left by the numerous setbacks in the Starliner program.
In 2019, during a first uncrewed test flight, the capsule was not placed on the right trajectory and returned without reaching the ISS.
Then in 2021, with the rocket on the launchpad for a new flight, blocked valves forced another postponement.
The empty vessel finally reached the ISS in May 2022.
Since then, Boeing has been working on the crewed test flight so the capsule can be certified for NASA's use on regular ISS missions.
It had hoped to carry out that flight in 2022, but problems kept cropping up, notably in the parachute system used to slow the craft when it returns to Earth's atmosphere.
"There are a number of things that were surprises along the way that we had to overcome," said Boeing executive Mark Nappi.
"It certainly made the team very strong, and very proud of how they have overcome every single issue that we've encountered." he added.
"It's pretty typical that a human spaceflight vehicle from design to flying humans is about a 10-year period."
- 'Very embarrassing' -
NASA associate administrator Jim Free predicted the mission would not be hiccup-free.
"We certainly have some unknowns in this mission, things we expect to learn, being a test mission. We may encounter things we don't expect," Free said, noting that Starliner is just the sixth US-built class of vessel for NASA astronauts.
SpaceX's Dragon capsule joined that exclusive club in 2020, following the Mercury, Gemini, Apollo and space shuttle programs.
Once Starliner is fully operational, NASA hopes to alternate between SpaceX and Boeing vessels to ferry astronauts to the ISS.
In 2014, the agency awarded fixed-price contracts of $4.2 billion to Boeing and $2.6 billion to SpaceX to develop these capsules.
"Everybody thought Boeing was going to get there first," Erik Seedhouse, an associate professor at Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University, told AFP.
"And so that SpaceX got there way ahead of Starliner was very embarrassing for Boeing."
Even though the ISS is due to be mothballed in 2030, both Starliner and Dragon could be used in the future to taxi humans to future private space stations, which several companies are planning to build.
(V.Varonivska--DTZ)