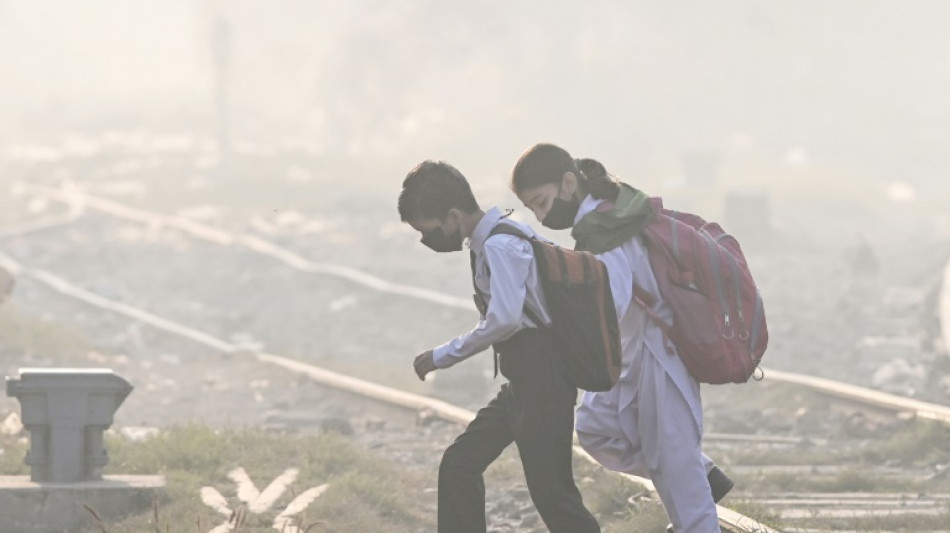
Pakistan reopens Punjab schools after smog improves

Schools reopened Wednesday in Pakistan's most populated province after authorities announced a drop in dangerous air pollution, with parents rejoicing their children's return to classes.
Punjab, home to more than half of Pakistan's 240 million people, closed schools in its major cities on November 6 after dense smog hit "hazardous" levels, a situation described by the province's environment minister as a "national disaster."
But Punjab's environmental agency said late Tuesday that "the ambient air quality had improved in Punjab" due to rain in the north, as well as change in wind direction and speed.
"Therefore, all the educational institutions in the whole province, including Lahore and Multan Division, shall be opened" beginning Wednesday, it announced.
By morning, smog still shrouded the Punjab capital of Lahore as commuters headed to work, while road tractors continued belching wafts of dark smoke.
However the Air Quality Index for Lahore was 150, reflecting a massive improvement from two week ago when pollution in the city climbed to a record-high AQI value of 1,100.
Parent Muhammad Waheed, 48, said his children were "happy when the announcement was made about schools reopening".
"The children were getting bored at home," the daily wage worker told AFP. "Thank God, they'll be going back to school."
According to authorities, students and staff will still be required to wear face masks.
There is also a "complete ban on outdoor sports and outdoor co-curricular activities till further orders", said the environmental agency.
Every Lahore winter, a mix of low-grade fuel emissions from factories and vehicles, exacerbated by seasonal crop burn-off by farmers, blanket the city, trapped by cooler temperatures and slow-moving winds.
According to a University of Chicago study, high levels of pollution have already reduced life expectancy in Lahore, a city of 14 million inhabitants, by 7.5 years.
But the issue is "not limited to Lahore alone", said Punjab's environment minister Marriyum Aurangzeb during a press conference Wednesday.
"Due to seasonal atmospheric conditions, it is also affecting southern Punjab, northern Punjab, Islamabad, Rawalpindi, Abbottabad, and now Karachi. The wind speed is also impacting Karachi," she said.
"This is a national disaster, and we must treat it as such. As a nation, we need to come together and take collective action to address this (smog)."
- 'Disrupted' education -
A steady stream of parents ferrying their children on motorbikes arrived at a Lahore school Wednesday, with staff members checking to see that the girls clad in blue uniforms had on face masks.
"It's good that schools are reopening, as children's education was being disrupted," said Muhammad Akmal, who had just dropped off his daughter. "Kids were distracted by their phones and not focusing on anything else."
Instead of closing schools, he said the government should have pursued other measures "such as using artificial rain to address the smog".
Breathing toxic air has catastrophic health consequences, with the World Health Organization (WHO) warning that strokes, heart disease, lung cancer and respiratory diseases can be triggered by prolonged exposure.
Even before smog descended on Pakistan, UNICEF reported that "around 12 percent of deaths among children under five were due to air pollution".
Two weeks ago, the Air Quality Index hit a record high of 1,110. By Sunday, it had fallen below 300 -- the threshold considered "hazardous" for humans.
Still, as of Tuesday evening, the concentration of PM2.5 micro-particle pollutants in Lahore was still more than 10 times higher than levels deemed acceptable by the WHO.
Similar hazardous conditions have hit India's capital New Delhi, where classes have been moved online after air pollution surged past 60 times the WHO-recommended daily maximum.
Experts believe that modernising car fleets, reviewing farming methods, and making the transition to renewable energies are key to overcoming the smog that paralyzes millions of Pakistanis and Indians every year.
strs-vid-stm/dhc/mlm
(L.Møller--DTZ)