Massive Australia wildfires increased Antarctic ozone hole: study

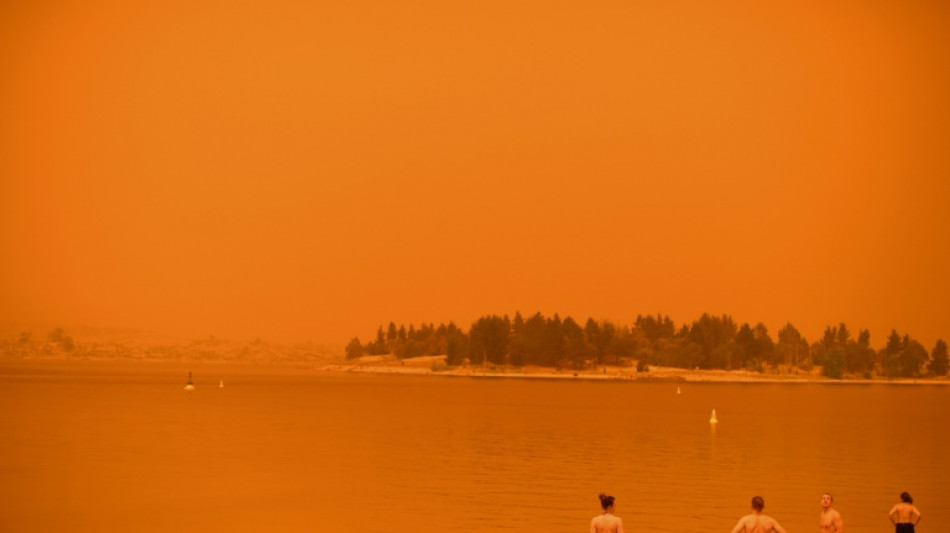
Smoke from monster wildfires in Australia caused a chemical reaction that widened the ozone hole 10 percent, researchers said Wednesday, raising fears that increasing forest fires could delay the recovery of Earth's atmospheric protection against deadly UV radiation.
Severe summer heat and drought helped drive the deadly "Black Summer" fires from late 2019 to early 2020, which destroyed vast swathes of eucalyptus forest and enveloped Sydney and other cities in smoke and ash for months.
Previous research concluded that more than a million tonnes of smoke pumped into the atmosphere by the fires prolonged the Antarctic ozone hole that opens up above Antarctica each spring.
In a new study, published in the journal Nature, researchers in the United States and China identified a previously unknown chemical reaction in the wildfire smoke that increased the depletion of ozone -- the atmospheric gas that reduces the amount of ultraviolet radiation reaching the Earth's surface.
Susan Solomon, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology professor who led the research, said that this reaction had chipped away at the edges of the ozone hole over Antarctica, expanding the hole by more than two million square kilometres (770,000 square miles) -- 10 percent of its area compared to the previous year.
"These chemical reactions are happening right on the edge of the region where the ozone hole happens," she said, explaining that the "particles give it a little extra push".
More broadly the study found that by triggering this reaction, the fires likely contributed to a three to five percent depletion of total ozone at mid-latitudes in the southern hemisphere, over Australia, New Zealand, and parts of Africa and South America.
The ozone hole was first created by human pollution -- particularly chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) emitted from many refrigerators -- but in recent decades, a global agreement on these manmade chemicals has given the ozone layer a chance to heal.
The 1987 Montreal Protocol, ratified by 195 countries, sharply reduced the amount of CFCs pumped in the atmosphere, although the molecules linger for decades.
United Nations modelling predicts that the ozone layer over the southern hemisphere should fully heal by 2060.
But Solomon, who first identified the chemicals responsible for the Antarctic ozone hole in the 1980s, expressed concern that the effects of climate change could slow that recovery.
"We think wildfires are going to become more frequent and intense," she told AFP, adding the ozone hole "will get better eventually, I believe, but it's conceivable that wildfires could certainly slow it down.
"I don't think it's going to stop the recovery altogether. But it could stop it from actually recovering when we think it should."
(A.Nikiforov--DTZ)