Mozambique detects polio case after Malawi outbreak

Mozambique has detected its first case of wild poliovirus in three decades, following an outbreak in neighbouring Malawi in February, the World Health Organization (WHO) announced Wednesday.
The case was diagnosed in a child in the northeastern province of Tete, it said.
"The detection of another case of wild poliovirus in Africa is greatly concerning, even if it's unsurprising given the recent outbreak in Malawi," WHO Africa chief Matshidiso Moeti said.
Poliomyelitis -- the medical term for polio -- is an acutely infectious and contagious viral disease which attacks the spinal cord and causes irreversible paralysis in children.
Wild polioviruses are viruses that occur naturally in the community, and typically spread when the faeces of an infected person contaminate water or food.
Africa was declared free of indigenous wild poliovirus in August 2020 after no polio cases had occurred on the continent for the previous four years.
However, unvaccinated people are still at risk if the virus enters their country from one of the few places in the world where the disease is still circulating.
The WHO said lab tests showed that the Mozambique case was linked to a strain that had circulated in Pakistan and led to the case reported in Malawi.
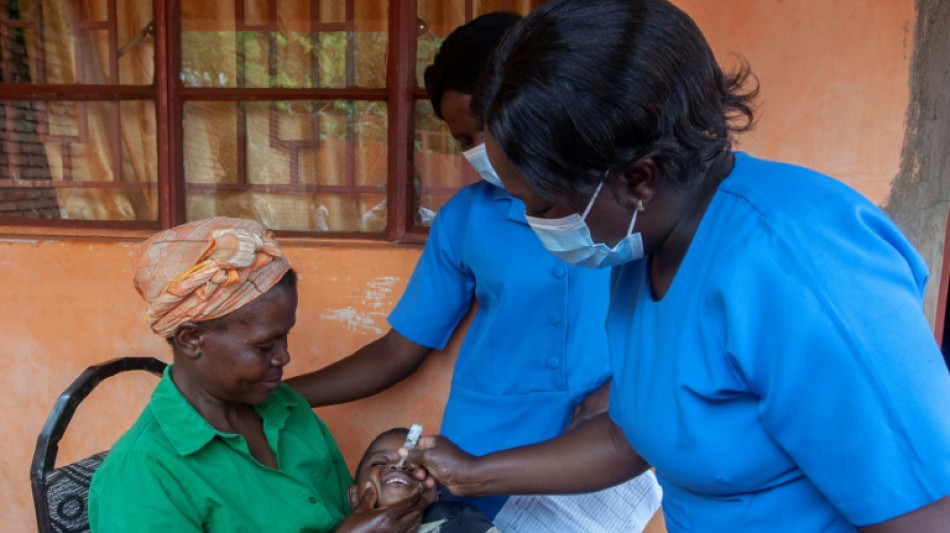
The outbreak in Malawi has prompted southern African countries to launch a vaccination blitz.
Malawi and its four immediate neighbours -- Mozambique, Tanzania, Zambia and Zimbabwe -- plan to immunise 23 million children aged five years or below. Mozambique alone hopes to vaccinate 4.2 million youngsters, the WHO said.
"As long as a single child remains infected with poliovirus, children in all countries are at risk of contracting the disease," the UN agency says on its website.
"The poliovirus can easily be imported into a polio-free country and can spread rapidly amongst unimmunized populations."
(V.Sørensen--DTZ)